You have developed a website and written content on it and acquired some quality backlinks but traffic is not increasing, and ranks are not improving. What can be the reason? Technical SEO? Yes, it can be as technical SEO is very crucial for SEO growth. This technical SEO guide will you understand implementing it in a very simple and detailed way. But before that, you will have to understand Search Engine Optimization.
Let’s understand what SEO is first. SEO is the actions performed on a website or mobile application to increase its visibility on the search engines like Google or app stores. Visitors that come to the website from search engine results are called organic traffic. We are now clear about SEO, but how do you start with SEO? SEO is divided into three parts – On Page SEO, Off Page SEO, and Technical SEO.
Most blogs will focus on on-page SEO, but technical SEO is also as important as other SEO practices and a very important part of SEO strategy, as technical SEO ensures the website crawlability and indexability by search engines. In this article, we will dive deep into technical SEO and discuss how you can optimize your website to make it accessible to users. Let’s understand technical SEO
What is Technical SEO?
Technical SEO ensures the three most important components of SEO, i.e., discovery, crawlability, and indexability. Discovery means that search engine crawlers like Google bots can find your website, and crawlability means that bots can understand the website content. Indexability is when the search engine adds the website to the SERP (Search Engine Results Pages). In short, technical SEO helps the website to be found with improved rankings.
Technical SEO looks like a simple term, but it’s not. However, it’s easy to master the basics, but it has a lot of complexities that can be resolved by SEO experts or a professional SEO Agency. In this technical SEO guide, we have tried to explain technical SEO very simply. Let’s start
Importance of Technical SEO
Imagine you have written a great piece of content, and this content is well researched that will educate the users. And you send an email campaign with the content link, but as users click the link to read the article. It takes 20 seconds to load the page. Readers become impatient and hit the back button and return from the website without reading your content or taking any action on the website.
It increases your bounce rate because every additional second in loading time increases the bounce rate. It results in a loss of traffic and losing out on potential leads and can also impact your organic ranks. From the above example, it is clear that great content also is not useful if the website is not optimized for technical SEO properly.
Because, without technical SEO Google can’t find, crawl and index the webpages. It’s important to focus on technical aspects of the website, such as page load speed, user experience, broken navigation, core web vitals, mobile friendliness, security, broken links, and duplicate content.
Additionally, Technical SEO is vital in creating a positive user experience. Optimizing for site speed and mobile-friendliness, for example, can help improve the overall user experience and increase the likelihood that visitors will engage with a website. Technical SEO will become even more important as search engines prioritize the user experience in their ranking algorithms. In short, Technical SEO is the foundation of any good SEO strategy.
By addressing technical SEO issues and implementing best practices, businesses can improve their website’s visibility in search results, drive more organic traffic, and ultimately increase conversions and revenue. You cannot ignore technical SEO in 2023 because ignoring the technical SEO strategy will hurt Google, and hurting Google can penalize your website. Let’s understand important technical SEO factors.
Technical SEO factors
We divide the technical SEO into three different categories:
- Crawlability
- Performance
- Indexation
Crawlability
Crawlability measures how efficiently Googlebots or other search engine bots crawl your website. Crawlability includes: –
- Java Script
- Links
- Site Structure (URL Structure)
- Redirects
- Server Error
- Crawl Budget
Performance Includes: –
- AMP
- Responsiveness
- Site Speed
Indexation Includes: –
- Sitemaps
- Internal Linking
- Duplicate Content Issues
First, we will talk about site structure.
Site Structure
Site structure is one the most important aspects of technical SEO that should be decided in the development phase. Site structure is the most basic concept because a poorly designed site structure can ruin the user experience and also confuse the crawlers. It also impacts other factors, such as sitemaps, robots.txt, breadcrumbs, and user experience. The best practice is to keep a flat structure on the website. It means that there should not be much depth in your URLs because it makes the discoverability of some pages difficult. 
URL Structure
URL are referred to as Uniform Resource Locator; they are responsible for giving information about the webpage to the visitor and search engine. URL is divided into the protocol, sub-domain, domain name, sub-folder, and page/path name. 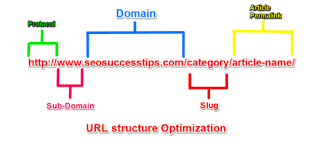

Breadcrumb Navigation
Breadcrumb navigation is important to include on web pages for two reasons. It tells users the path they have followed to reach a particular page, and second, users can click on the path anytime to go back to the previous page or the main page. 
Crawling, Indexing, and Rendering
Crawling
When Google bots visit the website, they should be able to crawl the website without any restrictions. Google bots use the links to jump from one page to another like a normal user. So ensure that all the links on the website are properly optimized and that there are no broken links, redirection loops, and redirection chains. For smooth crawling, you must ensure that Google bots are not blocked using robots.txt.
Robots.txt
Robots.txt file instructs the search engine where they can go on the website and where they can’t. Robots.txt helps block the pages not to be crawled, optimize the crawl budget, and resolve issues like parameterized URLs.
Crawl Budget
Crawl budget is often discussed in the SEO community, and it seems difficult to understand the topic. Let us simplify this term for you. Crawl budget is the budget crawlers use to crawl your website, and it’s different for all websites as Google decides it on several factors, like how much crawling your website allows and how accessible your website is for Google bots.
As a website owner, you will want all the important pages of the website should be crawled frequently, and other non-important pages should be crawled less. There are a few ways to optimize the crawl rate (the frequency with which Google crawlers crawl the website) and improve the frequency.
Properly interlink your website; even the deep pages should be linked properly, optimize the sitemaps and ensure JavaScript doesn’t affect the crawling. Now, Google bots have completed crawling the website; the step after this is indexing.
Indexing
Indexing refers to the action in which, after crawling the website, Google submits the website to its repository and makes it eligible for ranking on SERP. You need to ensure that Google properly indexes your website. You can check the indexation status of the website using a free tool provided by Google. i.e., Google Search Console.
In Google Search Console, you will get a coverage report from which you can figure out the pages indexed by Google and not indexed by Google, and it also gives the list of pages with indexing issues. 
Robots directive: <meta name= “robots” content=”no index” /> Sometimes, Google also might choose not to index your website despite of index and following instructions by the robots’ directives. Reasons for this can be canonicalization, duplicate content, thin content, mixed content, redirect loops and chains, webpage not mobile friendly, or HTTP error.
You can check how Google indexes your page using the Inspect URL option in the Google Search Console. Let’s understand each of these issues in detail
Canonicalization
If there is more than one version of the same page, then Google might choose the most relevant page for indexing according to it. You can see the version Google has preferred for indexing in Google Search Console. When you put your URL in the inspection tool, Google will give the report saying the user declared canonical and Google selected canonical. To ensure, Google indexes the version you want, you need to add the proper canonical tags on the website.
Duplicate Content
The website should not have duplicate content as it can confuse the search engine and impact its indexability. If you have two versions of the pages, then add a canonical tag to the less preferred version. The duplicate content issue mostly happens due to multiple versions of the same URL. Example: –
- https://example.com – Non-www HTTPS version
- http://example.com – Non-www HTTP version
- https://www.example.com – www HTTPS version
- http://www.example.com – www HTTP version
- https://www.example.com – without slash
- https://www.example.com/ – with a slash
Here, you can see six versions of the same page having the same content, but these all will be considered separate pages by Google, and it will index all of them, creating the duplicate content issue. Make sure to keep only one preferred version to avoid such issues.
Redirects
You need to make sure that all the redirects on the website are properly optimized. There should not be any redirect chains, loops, or broken links. It will impact the indexing of the website as it will confuse the search engines. You can use Semrush Site Audit tool to find all the redirection and broken links errors. Also, take care that there should not be any temporary redirects for the permanent changes on the website. Your sitemap should not contain any broken links or redirected URLs.
Mobile Responsiveness
One of the most impactful Google’s SEO Algorithm updates is Mobile-first indexing. As Google gets 55% of mobile traffic, it’s important for webmasters to optimize the website for mobile. If your website is not optimized for mobile, then Google will hesitate to index it, and there is a probability that it won’t index it.
In simple terms, optimizing the website for mobile is one of the most important technical SEO factors for indexing. There are tools to check the mobile-friendliness of the website. Google search console has a feature called Mobile Usability that lets you track the number of mobile-usable pages and pages that are not mobile-friendly.
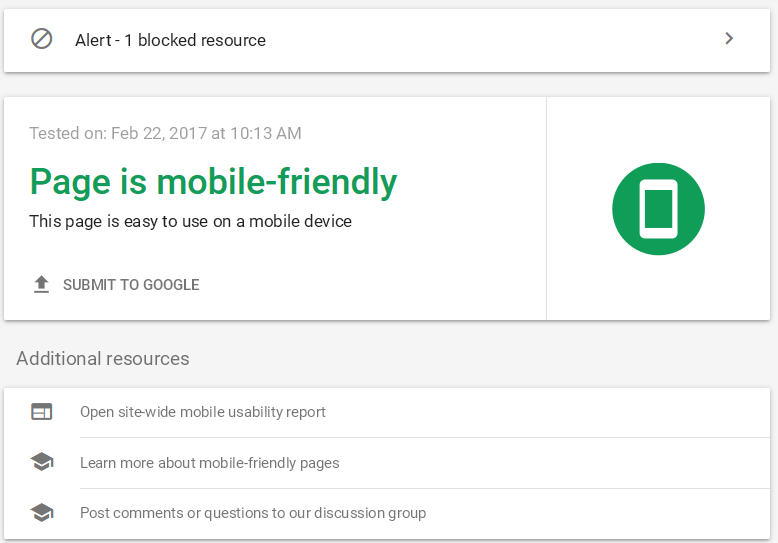
Most of the item’s issues will be clickable items nearby or text not readable that are easy to resolve, but sometimes there can be bigger issues to make sure to check the issue raised in GSC.
HTTP Errors
There are a lot of HTTP errors, such as 301, 302, 403, 404, 405, 500, 502, 503, and 504. All these errors can impact the indexability of the website. Let’s look at each of the errors in detail: – Permanent Redirects (301) – 301 Redirects is the most common status code you will notice in your crawl report after 200.
It permanently sends the shifting of the URL from one URL to another. For example, there is a link mentioned to the page URL 1 on the home page of the website, but the URL is 301 redirected to URL 2, so when the user clicks on the link of URL 1, they will directly land on the URL 2 page. It is called permanent redirection. It is not the issue as an SEO; you will have to redirect pages in multiple scenarios, one of which can be website migration or a change in the site structure. It becomes an issue if: –
- There are a lot of redirects on the website.
- Redirection chains – Redirection chains are created when the source URL doesn’t directly land on the destination URL, but before reaching the final destination, it goes to multiple URLs. Example: – URL 1 is redirected to URL 2, but URL 1 first gets redirected to URL 3, then URL 4, URL 5, then goes to URL 2. It slows down the website and negatively impacts the SEO. The solution for this is directly redirecting the source URL to the destination URL.
(Image : URL 1->URL 3->URL 4->URL 5->URL 2)
- Redirection loops – Redirection loops are created when the source and destination URL are the same. For example, URL 1 is redirected to URL 2 but finally comes to URL 1 only. The solution for the redirection loop is to properly remove the redirection from the source URL or redirect the source URL to the destination URL.
(Image:- URL 1->URL 2->URL 1)
- Broken links – There is an existing link on the page, but when the user clicks on this, it takes the user to a 404 page or 500 pages. It is called a broken link. The solution to resolve this is to remove the broken links from the webpage or replace them with relevant links.
As all these issues will slow down the website and can confuse search engines that can, resulting in crawling and indexing issues. You can use SEO audit tools to recognize the redirection errors, but if you want to know the path of a single page, then the redirect path chrome extension is the best solution. Temporary Redirects (302) – If you want to navigate users to different pages for some time, you can use 302 redirects.
It clearly tells Google that this setup is only for some time, so the indexability of your original page is not affected. It becomes an issue if, for permanently redirected pages, 302 is used. In this case, you should change the status of 302 to 301. Forbidden Message (403) – It means requested content is not accessible due to server misconfiguration or permissions. Error Pages (404) – This is another common error message you will get; it occurs if the page requested by the user is unavailable, removed by webmasters, or in case of the wrong URL.
It is also not an issue but becomes one of the 404 pages is not properly built. Method not allowed (405) – The server recognizes the request but then also blocks the access. Internal Server Error (500) – `This error occurs when the server cannot deliver the requested webpage. Bad Gateway Error (502) – This occurs when there is an invalid response Service Unavailable (503) – It means the server is okay, but currently, it is not able to serve the request Gateway Timeout (504) – There is a time lag between the server and your web server, due to which the request cannot be completed.
You need to find these errors in your website’s technical SEO audit and resolve them to keep your user experience and website accessibility intact and search engines happy. Now the website is crawled and indexed, you need to see how Google renders your website. Let’s move on to renderability.
Rendering
Once Google has completed crawling and indexing the website, the third step is rendering. In Rendering, Google shows the indexed content to the users. Rendering has become important as websites now have complex JavaScripts, and Google faces issues in rendering complex Java Scripts. To solve this issue, Google recommends implementing pre-rendered content. Here is the list of issues that can impact the renderability of the webpage:
Load Time and Page Size
Load time not only affects your bounce rate but also impacts the crawlability of the webpage. If your web page takes too long to load, it ruins the user experience, and also crawlers don’t crawl it 100%, due to which chances of missing the crawl of important content are high. It’s important to keep the load time minimum to ensure the best user experience and allow crawlers to completely crawl the page.
Orphan Pages
Orphan pages are pages that don’t have internal links pointing to them. Due to no links, crawlers cannot discover these pages, crawl and index them. You can use the screaming frog and other SEO audit tools to find the orphan pages. Now, we are clear with three technical SEO elements Crawlability, Indexability, and Renderability. Let’s look at some more elements that are essential for your site.
Implement Hreflang Tags for International Websites
The Hreflang tag is the solution if your website is multilingual and has a presence in multiple countries. This tag will inform Google about the variations and avoid duplicate content or canonicalization issues. Implementing hreflang tags is not easy, but tools like technical SEO hreflang generator helps in generating and validating the hreflang tags.
Structured Data
Many SEOs think that implementing structured data will help them rank on the first page, but that’s not true. Structured data helps your website to show rich snippets that can improve CTR. Schema markup helps search engines like Google understand the data and content on the website. Different types of schemas are available depending on page type, like business, events, people, products, reviews, videos, recipes, article schemas etc. You can use Schema Markup Generator Tools to create the schema and Schema validator tools to validate it.
JavaScript Rendering
JavaScript can sometimes block the crawlers and make it hard for them to crawl the website properly. One of the best solutions to improve JavaScript website crawlability is server-side rendering.
Other Technical SEO Factors
XML Sitemap
In this article, we have talked a lot about sitemaps and the importance of sitemaps in technical SEO. The XML sitemap is undoubtedly a very important part of SEO. It also wears multiple hats, so it’s important to create an XML sitemap properly and revisit it monthly to resolve issues. An XML sitemap helps search engine crawlers to crawl the website faster, resulting in faster indexing, categorizing the pages, and organizing large websites. It’s also important to optimize the XML sitemaps. Here are a few tips to optimize the XML sitemaps: –
- Create a sitemap according to page categories; for example, there can be a different sitemap for blog pages and product pages.
- Keep important pages on the top of the sitemap.
- Only include the canonicalized version of the web pages, and don’t add index pages in the sitemap.
- Dynamic sitemaps are the best option for large websites.
You can create a sitemap using Sitemap Generator tools, or Yoast SEO will do the job for you if you have a WordPress website. It’s important to validate sitemaps from time to time to look for 404 or 301 status codes. It should have all the 200 status code pages without any no index or error pages. You can use the Map Broker XML Sitemap Validator tool to check your sitemaps.
Core Web Vitals
However, we discussed core web vitals earlier in the article, but here we will discuss them in detail. Google announced Core Web Vitals on May 28, 2020, one of the most important ranking factors. Core Web Vitals is made of three user experience factors and page speed: Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS). These three factors define the loading of a webpage, interactivity and visual stability. These vitals ensure that the webpage provides the visitors with the highest user experience.
Google has also introduced Core Web Vitals report in Google Search Console that tracks Core Web Vitals for all the website web pages. This report segregates the URLs into poor ones that need improvement and good ones. Using this report, you can prioritize your efforts on improving the page speed and Core Web Vitals.
Reduce Webpage Size
Big webpages take time to load, creating issues like increased page speed, bad core web vitals, and increased bounce rate. There are methods to reduce webpage size, like implementing CDN, caching, lazy loading, and minifying CSS. There are other factors, such as eliminating 3rd party scripts and removing unnecessary JavaScript.
On Page Factors
There are few on-page factors that should be covered in the technical SEO audit. These factors are missing tittle tags, meta descriptions, missing image alt text, long or short title tags and meta descriptions, parametrized URLs
Technical SEO Tools
Here is the list of all the SEO tools you will need to conduct a technical SEO audit.
Google Search Console
Chrome DevTools
Chrome DevTools is a tool to debug website issues such as page speed, performance issues, and others.
Mobile-Friendly Test
Google Mobile-Friendly Test is a free tool by Google to check the mobile-friendliness of webpages. This test tells you the issues such as small text, clickable buttons too close, etc.
Page Speed Insights
Page Speed Insights is a free performance tool by Google that observes the webpage and provides the page speed scores for both mobile and desktop versions. This tool tells in detail the reason for the slowdown of a webpage and optimization opportunities. Page Speed Insight (PSI) also gives the score of vitals. And tells you if your webpage passed the Core Web Vitals Assessment or not.
Metrics it measures are Largest Contentful Pain (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS), First Contentful Paint (FCP), Interaction to New Paint (INP), and Time to First Byte (TTFB). Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) – LCP is the time taken to load the page’s main content and the time it takes for interactivity. The important point is that video and SVG are not considered while calculating the LCP. First Input Delay (FID) – FID or input latency is the time a browser takes to respond to the first interaction with a website while it is loading.
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) – The CLS occurs when webpage elements unexpectedly shift while downloading. Fonts, images, videos, contact forms, buttons, and other kinds of content tend to shift. First Contentful Paint (FCP) – FCP refers to how long it takes for a user to see the first content on a website, whether it’s images, text, logos, background graphics, or elements outside the white canvas.
Interaction to New Paint (INP) – The INP metric is a new Core Web Vitals metric that measures a page’s overall interaction delay. Time to First Byte (TTFB) – TTFB indicates how long your browser takes to receive the first byte of a response from a web server when you request a particular URL on a website.
However, page speed score or core web vitals assessment is not the ranking factor, but yes, good page speed scores and better core web vitals are ranking factors. Page Speed Insight is not the only tool to measure webpage performance. There are other third-party tools, like GT Metrix and Pingdom Speed Test.
Screaming Frog
Screaming frog is undoubtedly the best website crawler and is an essential tool for auditing websites for technical SEO. If used properly, you can crawl and find every nook and corner of your website. It tells you everything from total URLs on the website, indexed URLs, not indexable URLs, URLs blocked by robots, inlinks, and outlinks, and fetches all the on-page elements like titles, descriptions, and heading tags. This vast tool can help you with almost anything in SEO. Use it wisely to improve the technical SEO of your website.
Semrush
Semrrush is the most popular SEO tool, and its site audit feature makes technical SEO audit very easy. It gives a detailed report of all the errors and warnings that may impact your website. It also gives a site health score based on current issues on the website. This score is a good indication to measure your progress on technical SEO. The tech audit report will also tell you the issues to be addressed on priority and low or medium-priority issues. It measures your website on the following factors – crawlability, HTTPS, international SEO, Core Web Vitals, Site Performance, Internal Link, and Markup. You can also use the Ahrefs site audit feature; both tools are equally good.
Technical SEO by Merkle
Technical SEO by Merkle is a less-known but easy-to-use and handy tool for SEOs. It has different tools which will make your life easy. Tools provided by technicalseo.com are robots.txt tester, .htaaccess tester, sitemap generator, RSS Feed Parser, Fetch & Render, Pre-rendering tester, Mobile-First Index Tool, Mobile-Friendly Test, Bulk AMP Validator, Hreflang Tags Tester, Local-Adaptive Tester, Local Search Tool, Review Link Generator, SERP Simulator, Knowledge Graph Search, Schema Generator and Algo Update Tracker.
Features provided by this tool are not provided by any other tool, and it saves a lot of time while implementing the technical SEO recommendations. The best feature of this tool is the Local Search Tool, which allows you to view the SERP page of any location. It is very useful when you are working on international SEO.
Useful Chrome Extensions for Technical SEO
Technical SEO tools help you when you are working on large websites or enterprise SEO. Still, chrome extensions are very handy while analyzing the technical SEO for a single webpage or small website. Here is the list of Technical SEO chrome extensions:-
Meta SEO Inspector
Meta SEO inspector extension helps you extract meta information of the page, highlight issues, and also gives the advice to fix them. Some common errors it covers are title tags, meta descriptions, heading tags, canonicals, structured data, hreflang tags, etc.
Hreflang Tag Checker
Hreflang Tag Checker is one of the best chrome extensions for checking the hreflang tag implementation. It crawls the code, checks if the tag is correctly implemented, and links back to the right page.
SEO Minion
It checks the on-page SEO data and highlights the broken and outgoing links. The best feature of SEO Minion chrome extension is exporting the “People Also Ask” query from SERP on a particular keyword.
SEO Search Simulator
SEO Search Simulator by Nightwatch extension can help you find search results from any location globally for a particular keyword. It allows you to monitor the website ranks in different regions.
Redirect Path
Redirect Path tells you the exact path page follows before appearing to you. It will tell you if there is a redirect or redirect chain.
View Rendered Source
View Rendered Source extension is useful for heavy Javascript sites as Google crawlers face issues while crawling the Javascript. This extension shows you the difference between the rendered version of the code and the original code.
Final Thoughts
Conducting a quarterly technical SEO audit is crucial to ensure that your website is error-free and maintains accessibility. It becomes more important if you see today’s SEO landscape, which is changing rapidly with Google SEO algorithm updates. Technical SEO is not a simple and easy concept to master in a day; it takes time and a lot of practice. But you don’t have to do it alone; you can always take help from Pentra SEO services for your website SEO.
Some key takeaways about technical SEO website crawling and indexing is most important because if the content is not indexed, Google won’t rank it. Fix the broken things on the priority that might confuse users and crawlers. Build the website according to users, not search engines, as Google is focused on providing a better user experience.