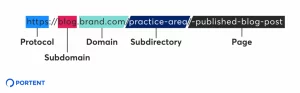
Subdomain vs. Subfolder is one of the most common wrangles we have faced while communicating to clients in SEO.
This argument arises whenever clients migrate their website, add a new section to the website, or launch new blogs or products.
Another common doubt is which website hierarchy is better for SEO, Subfolder, or subdomain and what Google thinks about it.
As an SEO agency, we have explained the difference between subfolders and subdirectories and how it impacts SEO based on our experience.
As you read this guide, expect to learn about the difference between subdomains and subfolders and how they impact SEO. Let’s first understand subfolders and subdomains and then dive deep into how they affect SEO.
Jump in!
What is a Subfolder?
Subfolders are a part of the main domain, lie under the root directory, and are considered the same domain or website by Google. For example, the subdirectory URL will be /blog that will lie under the main domain itself.
Example of Subfolder:- https://www.pentraseoservices.com/blog/
Subfolder URL Structure
Subfolder comes after the main domain or root directory in the URL structure. The subdirectory under the main domain signifies the website navigation in the URL; if the URL has a subdomain example:- /blog, then it says that all the URL slugs after the Subfolder, i.e., “/blog” will be the blog URLs.
There can be more than one Subfolder under the same domain—for example, www.yourdomain.com/services/seo. Here there are two folders under the root directory services and SEO.
What is Subdomain?
Subdomains are also a part of the website’s root domain, but it doesn’t follow the folder structure on the website. Subdomains usually act as separate websites and will have a different content management system, analytics, search console, and other tracking tools.
Subdomain URL Structure
Subdomains follow a flat structure. You will have a subdomain name followed by a root directory in the subdomain URL structure. Subdomains don’t contain folders within themselves and are on the same level.
Now that we have understood subdomains and subfolders, let’s look at how SEO differs in both cases.
SEO for Subdomains
There is no predefined SEO rule for subdomains and subfolders. They are used separately in different scenarios and according to the need of the business.
However, subdomains are considered separate entities, and even search engines track and crawl them as different domains.
As subdomains are considered separate entities, they need separate tools for tracking. You will need to set up a new Google Search Console for a subdomain, and even while adding the project in SEO tools like Semrush, subdomains will be considered separate.
Subdomains might not affect the authority of your main domains, and they won’t be able to pull up or pull down the authority of the root directory.
Now the question is, In which scenarios should webmasters use subdomains?
Why Use Subdomains?
Subdomains can benefit big websites running multiple businesses or publishing sites with content related to different niches. They can also be beneficial if you run campaigns or launch a product requiring complete new branding.
Subdomains are favorable if you have a relevant business requiring different content and branding from the primary domain.
When to Use Subdomains?
You can use the subdomains in the below-mentioned scenarios:
1. Support
2. Events
3. Blogs
4. Campaign Pages
5. Different Geographic pages
6. eCommerce Stores
Let’s look at each of the cases in detail:-
Support
Some business doesn’t want to keep support on the primary domain. There can be a few reasons behind it; the audience for support of a website is completely different as support is required by customers while the website largely intends to bring in leads.
For example, Google has a separate subdomain for translation services (https://translate.google.com/); the primary reason for that can be that Google is a search engine, and the translation business won’t match its search engine line.
Events
Event pages are short-lived and don’t hold much value when it comes to SEO. So, most businesses prefer to keep them separate.
For example, Hubspot uses a separate subdomain for its events section https://events.hubspot.com/.
Blogs
Many companies like to keep their blog section in subdomains. Reasons behind it can be that they want to use separate CMS for the blog section, keep separate tracking for blogs, and create authority through their content.
For example, Cloudflare uses a subdomain for blogs https://blog.cloudflare.com/.
Ecommerce Store
Few companies sell other products or merchandise with their products, so they prefer to host their eCommerce stores on a subdomain.
For example, Hubspot has its merchandise store, and it is hosted on the subdomain https://shop.hubspot.com/.
Campaign Pages
Business running regular campaigns keep their landing pages separate so that it doesn’t mess up with their primary domain SEO.
Different Geographic Locations
It’s a good idea to target different geographic locations; it is helpful as it helps in easy tracking and optimizing. A German version of an English website will make more sense on a subdomain than on a subfolder.
For Example, Craiglist uses the same kind of structure:- https://orangecounty.craigslist.org/.
Subdomains vs. Subfolders
There is no robust answer to this, as subdomains host the type of content that is different from the root domain or the content that is unrelated to the primary domain. The subdirectory manages the content in the subfolder structure and remains under the root directory.
According to technical SEO, both approaches are right, but before deciding to move to a subdirectory or Subfolder, you need to look at the SEO impact.
How do Subdomains and Subfolders Impact SEO?
Google clearly says that it treats both structures equally, and there are no guidelines from Google on subfolders vs. subdomains.
But let’s understand a few points on how these effects SEO.
Subdomains are treated as separate domains, so it doesn’t get affected by authority, content, or backlinks of the primary domain and vice versa is also true. It means you will need a separate SEO strategy and team to manage professional SEO services for subdomains.
Most businesses will host different content on subdomains and target a different set of keywords from the primary domain and subdomains, but if you publish the same content on both entities, then subdomains and the main domain might compete against each other.
Subdomains are a good choice if you are running multiple business lines and want to manage your website separately.
At last, if you don’t have a large website and multiple product lines, then we would recommend having a subfolder structure, as it will be easier for your SEO team or SEO agency to manage one website and improve its authority rather than working on multiple domains, and this will save cost and time both.
Before moving ahead, let’s hear from Google about subfolders and subdomains.
Google View on Subdomains vs. Subdirectories
There are many myths floating around subdomains, and subfolders like subdomains befuddle the Google bots, and they are not able to crawl the subdomains properly hence affecting the indexing of subdomains.
However, Google says it doesn’t discriminate between subdirectories and subdomains and treats them equally.
Here is a video by John Muller, Google Webmasters Trends Analyst, who mentions that both site structures are equal for Google.
https://youtu.be/uJGDyAN9g-g – (Embed this link in the CMS)
Now that you are clear with subdirectories and subdomains, their effect on SEO, and how Google treats them, it should be easy to decide between the two options.
Conclusion: Which is better, Subdomains or Subdirectories
Again, this is a confusing and debatable topic, but we have tried explaining both types of structures in detail to ease your decision.
Subdomains can help you improve navigation on a website and manage content better if you have a large website with multiple businesses. Subfolders are best for a smaller website, not having much content and various business lines.
Whatever you choose, you can also be on top of your SEO with the right SEO and content strategy.